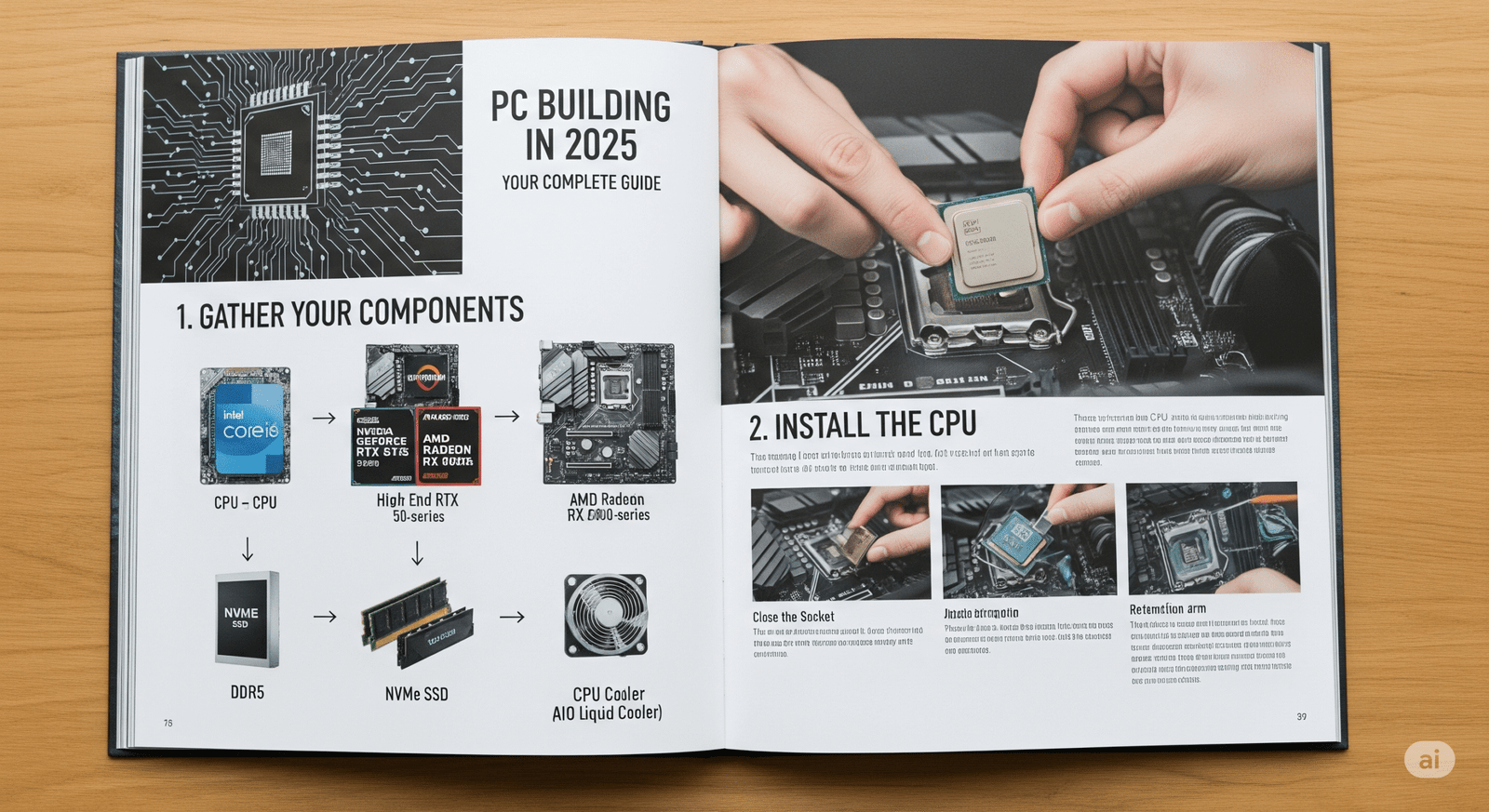
Building your own PC might seem like a daunting task, but in 2025, it’s more accessible and rewarding than ever. Not only can you tailor your machine precisely to your needs and budget, but you’ll also gain a deeper understanding of how computers work. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and considerations for building your dream PC in 2025.
Why Build Your Own PC in 2025?
- Customization: Choose every single component to match your specific requirements, whether it’s high-end gaming, video editing, or everyday productivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often, building your own PC can provide more performance for your money compared to pre-built systems.
- Upgradability: Easily upgrade individual components as technology advances, extending the lifespan of your PC.
- Learning Experience: The process of building a PC is a fantastic way to learn about computer hardware and troubleshooting.
Key Components You’ll Need:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The “brain” of your computer. Choose between Intel and AMD based on your budget and performance needs. Research benchmarks for the latest generation processors.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all other components. Ensure it’s compatible with your chosen CPU socket and has the features you need (e.g., RAM slots, expansion slots, ports).
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Crucial for multitasking and running applications smoothly. Determine the amount of RAM you need based on your usage (16GB is a good starting point for most users in 2025, with 32GB or more recommended for demanding tasks). Pay attention to the speed (MHz) and compatibility with your motherboard.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Essential for gaming and graphically intensive tasks. Choose a dedicated graphics card from NVIDIA or AMD based on your gaming resolution and desired frame rates. Integrated graphics on the CPU might suffice for very basic tasks.
- Storage (SSD/NVMe): Solid State Drives (SSDs), especially NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) drives, offer significantly faster boot times and application loading compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Consider a smaller, fast NVMe drive for your operating system and key applications, and a larger HDD for mass storage if needed.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Provides power to all your components. Choose a PSU with enough wattage to handle your system’s demands, with some headroom for future upgrades. Look for reputable brands and efficiency ratings (e.g., 80+ Gold).
- PC Case: Houses all your components. Select a case with good airflow, sufficient space for your parts, and aesthetics you like. Consider the size and form factor (e.g., ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX).
- CPU Cooler: Keeps your CPU from overheating. Options range from basic air coolers to more efficient liquid coolers, especially important for high-performance CPUs.
The Building Process (Simplified):
- Preparation: Gather all your components, tools (screwdriver, anti-static wrist strap), and a clean workspace. Consult your component manuals.
- CPU Installation: Carefully install the CPU onto the motherboard socket.
- RAM Installation: Slot the RAM modules into the designated slots on the motherboard.
- Motherboard Installation: Mount the motherboard inside the PC case.
- GPU Installation: Insert the graphics card into the appropriate PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- Storage Installation: Connect the SSD/NVMe and/or HDD to the motherboard and secure them in the case.
- PSU Installation: Place the power supply in its designated bay and connect the necessary power cables to the motherboard, GPU, and storage devices.
- Cable Management: Neatly organize the cables inside the case to improve airflow and aesthetics.
- Initial Boot-Up: Connect a monitor, keyboard, and mouse, and turn on the PC to ensure all components are functioning.
- Operating System Installation: Install your preferred operating system (Windows, Linux, etc.) onto your primary SSD.
- Driver Installation: Install the latest drivers for your motherboard, GPU, and other peripherals.
Tips for 2025:
- Research Emerging Technologies: Keep an eye on advancements in CPU and GPU architectures, RAM speeds (like DDR6 potentially becoming more mainstream), and faster NVMe Gen 5 SSDs.
- Consider PCIe 5.0: If you’re building a high-end system, look for motherboards and GPUs that support the faster PCIe 5.0 standard for increased bandwidth.
- Focus on Efficient Cooling: With increasingly powerful components, a robust cooling solution (either high-end air or liquid) will be crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
- Cable Management is Key: Modern cases often have features to aid in cable management. Take your time to ensure good airflow, which is vital for keeping your components cool.
Building your own PC in 2025 is a rewarding endeavor that offers unmatched control over your computing experience. By carefully planning your components and following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to creating a powerful and personalized machine.

